English 

T: +86-18367823571
E: lyy@xg1688.cn
E: lyy@xg1688.cn
Building 2, No. 84, Qingxi Dongfeng Road, Qingxi Town, Dongguan City, Guangdong Province, 523642, China



Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-07-18 Origin: Site
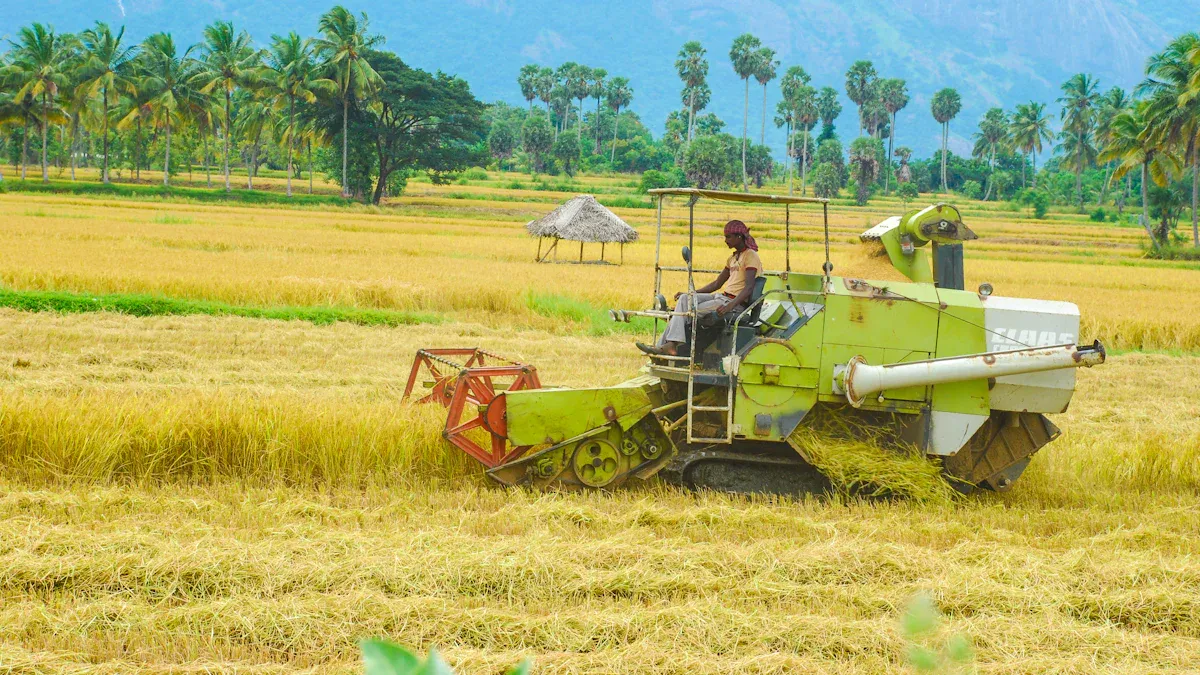











A rice transplanter is a machine that helps farmers by automating the process of planting rice seedlings in fields. This equipment lifts seedlings and places them into the soil with speed and accuracy. Farmers who use a paddy transplanter can save a huge amount of labor. In the past, planting rice by hand took about 2,000 hours per hectare, but with machines, this time drops to just 260 hours. The rice transplanter gives each seedling the same spacing and depth, which leads to healthier crops and better harvests.
Rice transplanters help farmers save time and work. They plant seedlings faster than people can by hand. The machine also puts the plants in straight lines.
Using a rice transplanter helps crops grow better. It puts seedlings at the right depth and space. This helps farmers get more rice from their fields.
There are walk-behind and riding types. Walk-behind models are good for small fields. Riding models are better for big farms. Riding models also save more work for farmers.
Farmers must get seedlings and fields ready before planting. They should also take care of the machine often. This helps the planting go well and fast.
Picking the best rice transplanter depends on field size and money. It also depends on what features the farmer wants. Smart controls and GPS help make planting more correct and easy.

A rice transplanter is a machine that helps farmers plant rice seedlings fast and evenly in wet fields. The machine picks up young seedlings from a tray. It puts them into the soil at the right depth and space. The rice transplanter has many parts that work together. These parts are the seedling tray, pickup unit, conveyor system, and planting unit. The engine and wheels help the machine move through muddy fields. Newer paddy transplanters use smart controls and GPS. This helps keep the rows straight and the planting correct.
A rice transplanter makes planting rice much faster and easier. It can plant a big area in less time than people can by hand. This saves farmers time and hard work, especially when they are busy.
The table below lists the main parts of a rice transplanter and what they do:
| Component/Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Seedling Tray | Holds young rice seedlings safely; controls seedling density and quality for efficient planting. |
| Pickup Unit | Gently grabs seedlings from the tray; ensures smooth and timely seedling delivery. |
| Conveyor System | Moves seedlings from tray to planting unit; uses sensors and controls for accuracy and speed. |
| Planting Unit | Places seedlings into soil at correct depth (~3.25 cm) and spacing; keeps seedlings upright. |
| Closing Wheel | Covers roots with soil after planting; ensures seedlings are protected and stable. |
| Engine and Power System | Provides power via diesel engine or tractor PTO; coordinates shafts and sprockets for steady speed (0.5-1 km/h). |
| Wheels and Traction | Special wheels/tracks prevent sinking in muddy fields; provide grip and smooth movement. |
| Steering System | Allows precise guidance; modern systems use GPS and smart controls for straight rows and turns. |
The main reason for a rice transplanter is to make planting rice easier, faster, and more even. Farmers use this machine so they do not have to plant by hand. The machine puts each seedling at the same depth and space. This helps the plants grow better and gives more rice at harvest.
Some main benefits of using a rice transplanter are:
Labor savings: The machine means fewer people are needed for planting. It also makes the job much quicker.
Uniform planting: Each seedling is put at the same spot and depth. This helps the rice grow evenly and makes it easier to care for the plants.
Yield improvement: Studies show a paddy transplanter can give about 26% more grain than planting by hand. The machine also helps avoid missing or hurting seedlings.
Better crop establishment: The rice transplanter makes sure most seedlings are planted right, with fewer floating or buried plants.
Environmental benefits: Using a machine uses less water and fuel than planting by hand. It also helps keep the soil healthy and lowers greenhouse gas pollution.
Note: Even simple paddy transplanters can help make planting more even and use less labor. This is good for both small and big farms.
Farmers in different countries use rice transplanters in their own ways. The chart below shows how China, India, and Japan use these machines:
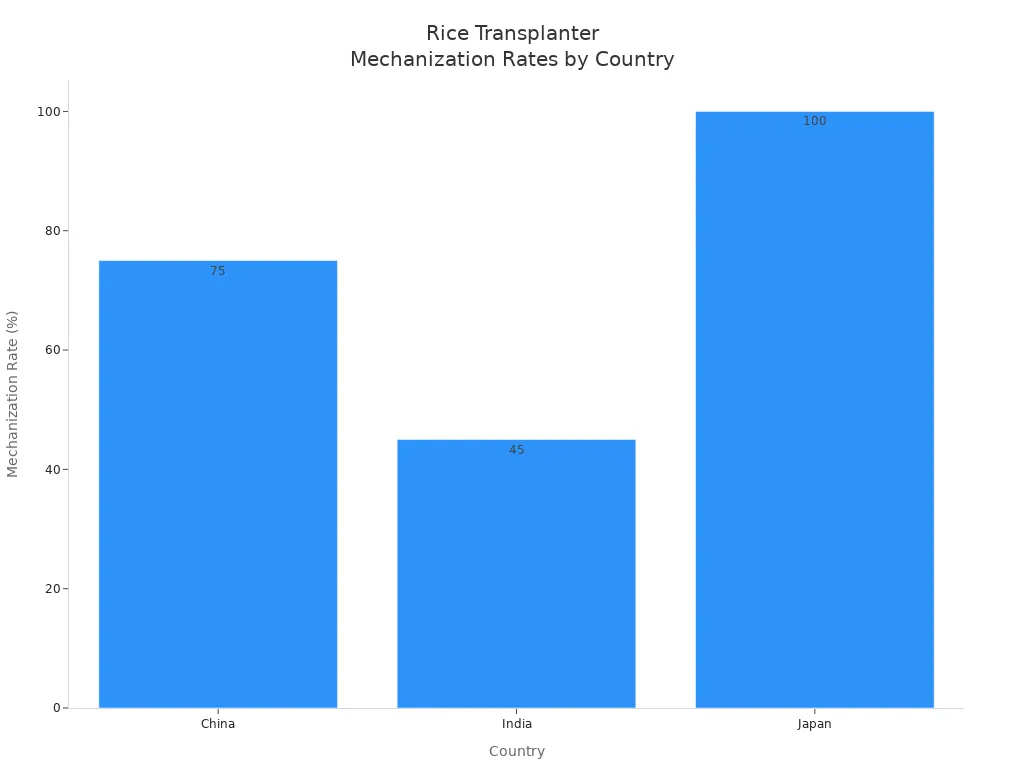
China uses many ride-on rice transplanters because of government help and bigger farms.
India is changing from hand planting to machines. More small paddy transplanters are used as it gets harder to find workers.
Japan is ahead in using smart machines with GPS for very exact planting.
The engine is the main part of a rice transplanter. Most machines use either a gasoline engine or an electric motor. Gasoline engines, like the MZ175®, give strong power between 3.3 and 4.0 kW. This helps the machine move well in muddy fields. Some models use electric motors. These are quiet and easy to control. A high-torque engine lets the transplanter work in tough fields. It keeps the planting speed steady. The engine powers the wheels and the planting parts. This helps the machine plant seedlings quickly and well.
| Engine Type | Model | Power Output (kW) | Power Output (PS) | Speed (rpm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gasoline OHV internal combustion engine | MZ175® | 3.3 (typical) / 4.0 (max) | 4.5 (typical) / 5.5 (max) | 3600 |
Big wheels and four-wheel drive help the rice transplanter move in wet fields. These wheels stop the machine from sinking. They also give strong grip. The wide pedal lets workers carry more seedlings. This means fewer trips are needed. A good suspension, like a four-wheel elastic suspension, absorbs bumps and shakes. This keeps the ride smooth and comfy, even for long hours. High ground clearance and a strong frame make the machine stable. They also protect the crops.
Tip: A good suspension helps the machine last longer. It also makes the operator less tired and the job easier.
The planting mechanism is very important in modern rice transplanters. It has many parts that work together. These parts make sure each seedling goes in at the right depth and space. The transplanting mechanism takes seedlings from the tray. It puts them in the soil with special claws. The seedling feeding part brings seedlings to the planting unit on time. Settings can be changed to control row space, hill space, and depth. Monitoring systems help keep the planting even. This helps crops grow better and gives more rice.
| Mechanism Component | Function / Description |
|---|---|
| Pickup Unit | Lifts seedlings from the tray with little root damage. |
| Conveyor System / Seeder Tray | Holds seedlings and keeps spacing the same. |
| Planting Unit | Puts seedlings in the soil in the right spot. |
| Closing Wheel | Covers seedlings with soil for good root contact. |
| Adjustable Settings | Controls spacing and depth for even planting. |
Modern rice transplanters are made for comfort and easy use. Seats and controls can be adjusted for different people. Hand and foot controls are close and easy to use. Vibration dampening systems help stop tiredness during long work. Clear displays and mirrors help workers see better. This lets them watch the planting and make changes fast. These features help workers stay comfy and do a better job in the field.
Walk-behind rice transplanter machines are small and easy to use. Farmers walk behind these machines to guide them in the paddy field. These models are good for small fields or places with sharp turns. The operator must walk a lot, sometimes up to 22 kilometers each day. New remote control systems help lower the work by about 18%. They also let the machine cover 20% more field. But walk-behind models still need more work than riding types. They move slowly at about 0.5 km/h and can plant 0.02 hectares each hour. These machines are best for small farms or tight spaces where big machines cannot go.
Note: Walk-behind paddy transplanters work well for small plots. They are a simple and cheap choice for farmers.
Riding rice transplanter machines let the operator sit and drive. This makes planting much easier. These machines are faster, moving at about 2.28 km/h. They can plant up to 0.222 hectares every hour. One person can use a riding model, which saves time and cuts labor costs by half. These machines use new technology for better planting and even seedling rows. They are best for big farms where speed and efficiency are important. Riding models also help finish planting on time, which keeps crop yields safe.
Advantages of Riding Models:
Plant seedlings fast and evenly
Lower labor needs and costs
Make planting more accurate
Save time during busy times
| Parameter | Walk-behind Model | Ride-on Model |
|---|---|---|
| Working Speed | 0.5 km/h | 2.28 km/h |
| Field Capacity | 0.02 ha/hour | 0.222 ha/hour |
Farmers can pick from different rice transplanter machine types. Manual walk-behind models have basic features for small fields. High-speed riding models, like the 2ZGQ©-6 (6-row) and 2ZGQ©-8 (8-row) High Speed Rice Transplanters, have more power and smart controls. These machines fit many farm sizes and needs. The right model depends on the field size, how many workers are there, and the money you can spend.
Tip: On big farms, a high-speed riding rice transplanter machine can save time and help you plant more.
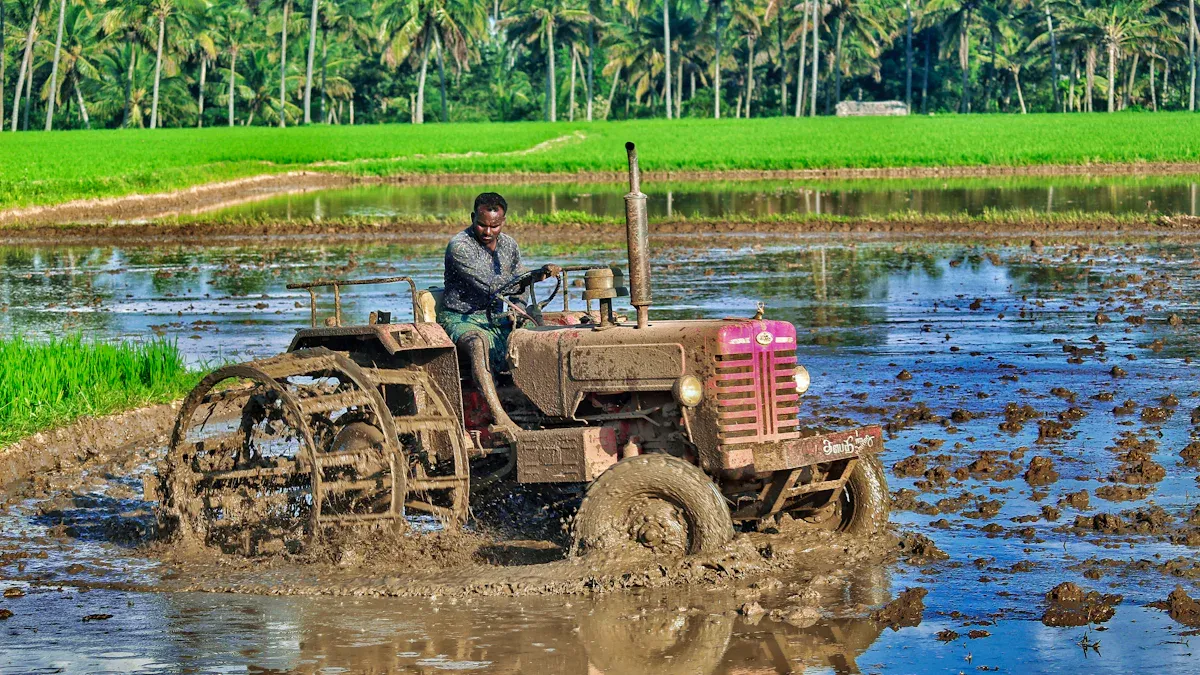

Farmers need healthy seedlings before using a rice transplanter. First, they get the field ready by tilling the soil. This makes the ground smooth for the machine. A smooth field helps the machine move and plant well. Next, farmers grow seedlings in nurseries. The seedlings should be 25 to 35 days old. Young and healthy seedlings grow better after planting.
Farmers also check the paddy transplanter before using it. They look at all the parts and add oil to moving pieces. They set the machine for the right depth and space. Good care stops the machine from breaking down. This helps the machine work without problems. Before starting, they check if the soil is wet enough. The right soil moisture helps the machine and keeps seedlings safe.
Tip: Farmers should watch the planting process. If there is a problem, they can fix it fast and keep planting.
Steps for preparing rice seedlings for mechanical transplanting:
Till the field to make the ground smooth.
Grow seedlings in nurseries until they are 25-35 days old.
Check and oil the rice transplanter. Set the depth and space.
Make sure the soil is wet enough.
After planting, control water, weeds, and pests.
The rice transplanter plants rice seedlings automatically. Farmers put trays of seedlings on the machine. The pickup unit gently takes each seedling from the tray. Then, the machine moves the seedlings to the planting part. The planting part puts each seedling in the soil. It plants them at the right depth, about 3 to 5 centimeters. The machine covers the roots with soil to keep them safe.
The rice transplanter makes sure every seedling is planted the same way. Hydraulic lifts and balance systems keep the depth steady, even if the ground is uneven. Farmers can change the row space, usually between 25 and 30 centimeters. This helps match different rice types. The machine can plant seedlings of different sizes and keeps planting even.
Planting by hand takes more time and hard work. Workers must bend and plant each seedling one by one. This often causes uneven planting.
Using a machine means younger seedlings from mat nurseries are used. The machine plants them fast and evenly. This saves work and helps crops grow better.
Machine planting also makes the rice ready sooner, sometimes 15 days earlier. It can give about 9% more rice than planting by hand.
Note: Both hand and machine planting need care after planting, like weeding and watering. But the rice transplanter makes planting much faster and more exact.
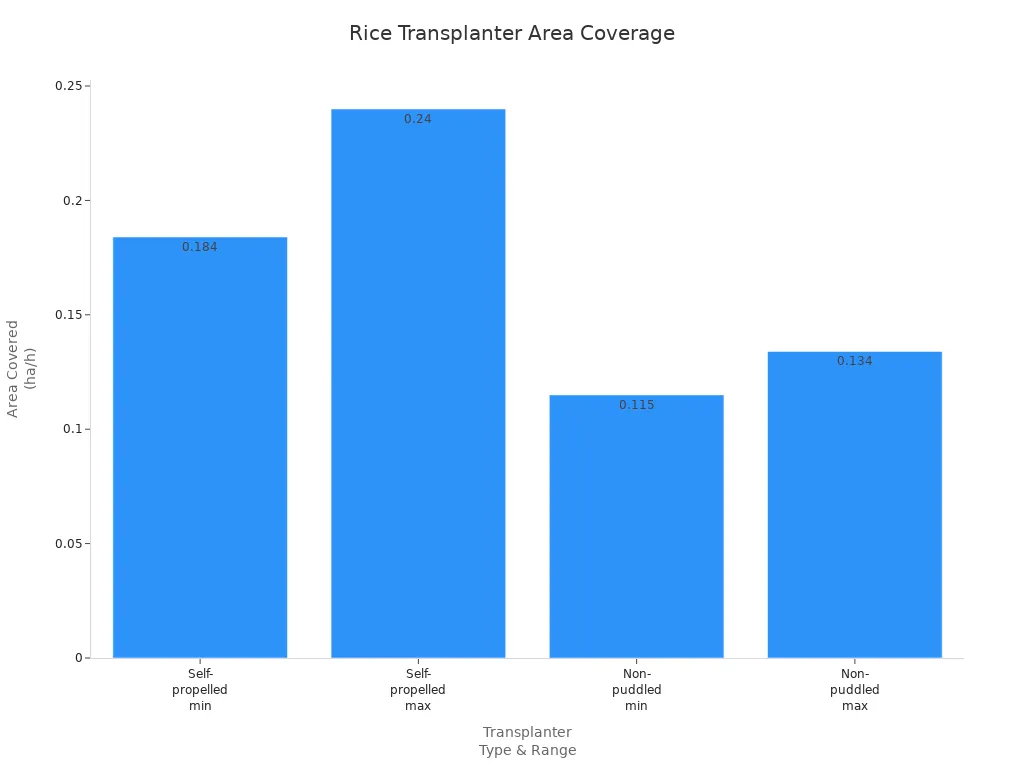
A rice transplanter helps farmers plant rice much faster. The machine can cover more land in less time than hand planting. Self-propelled rice transplanters can plant 0.184 to 0.24 hectares each hour. Field efficiency is between 65% and 83%, depending on the machine and field. The machine usually moves at 1.0 to 1.84 kilometers per hour.
| Parameter | Value Range / Specifics | Notes / Context |
|---|---|---|
| Effective Field Capacity | 0.184 ha/h to 0.24 ha/h | For self-propelled rice transplanters |
| Field Efficiency | 65% to 83.75% | Depends on machine and field conditions |
| Operating Speed | 1.0 km/h to 1.84 km/h | Speed during planting |
| Area Coverage in Non-Puddled Soil | 0.115 ha/h to 0.134 ha/h | More than in puddled soil |
| Missing Hills Percentage | Around 9.5% | Shows planting accuracy |
| Fuel Consumption | 1.66 l/h or 6.94 l/ha | Shows how much fuel is used |
Using a machine lowers costs by 25% to 30%. It also means less work and faster planting. The machine keeps missing hills low, about 9.5%. This means most seedlings are planted right. Farmers can finish planting on time and protect their crops.
Machine planting works in both puddled and non-puddled soils. In non-puddled fields, the machine covers more land each hour. This saves labor, fuel, and water costs.
Using a rice transplanter helps farmers plant faster and better. Automation makes planting even, which helps crops grow strong and makes the field easier to manage.
Farmers need to pick a rice transplanter that fits their field. Big fields with simple shapes let machines work fast. Small or odd-shaped fields slow the machine down. These fields may need more hand work. Steep slopes or hard-to-reach places make moving the machine tough. The type of soil is important too. Some machines work better in muddy or bumpy fields. Farmers should choose machines that can change planting depth and space. This helps them fit different field shapes. Training and good support help workers use the machine well.
Tip: Fields that are easy to reach and have simple shapes help the rice transplanter work better.
Rice transplanters come in many prices. Manual models are cheaper and good for small farms. Automatic machines cost more but save time on big farms. Extra features like GPS and smart controls raise the price. These features help plant rice faster and more evenly. Well-known brands may cost more but give better help and parts. Buyers should think about costs for fixing and learning to use the machine.
| Rice Transplanter Type | Price Range (USD) | Key Features and Suitability |
|---|---|---|
| Manual | 600 - 2,500 | Hand-operated, portable, best for small farms |
| Semi-Automatic | 2,000 - 5,000 | Walk-behind, moderate price, labor-saving |
| Fully Automatic | 5,000 - 20,000+ | Self-propelled, GPS, high capacity, large farms |
Farmers get better results by following easy steps. They should set the machine for the right number of seedlings. Lubricating and cleaning the machine stops it from breaking. Operators need to check and change planting depth and space for each field. Learning to use the machine safely helps avoid mistakes. Machines that are easy to fix save time when something breaks. Strong wheels and axles help the machine last longer. Cleaning trays and conveyors after use keeps the machine working well.
Note: Checking and caring for the rice transplanter often helps it plant evenly and last longer.
A paddy transplanter helps farmers plant rice quickly and evenly. Studies show that using these machines can cut labor by half and raise yields by up to 12%. Farmers also spend less on fuel. Smart planting tools make crop care easier and improve field management. Many farmers now choose a paddy transplanter to save time and boost harvests. They can talk to suppliers or test different models to find the best fit for their fields.
A rice transplanter plants seedlings much faster than people can by hand. The machine covers more land in less time. Farmers finish planting quickly and can focus on other important tasks.
Yes, one person can operate most rice transplanters. The controls are simple and easy to use. Some models even let the operator sit and drive, making the job comfortable.
Flat and open fields work best with rice transplanters. These machines move easily on smooth ground. Fields with many turns or steep slopes may slow down the machine.
Rice transplanters use healthy, young seedlings grown in trays. The seedlings should be about 25 to 35 days old. Tray-grown seedlings fit well in the machine and help it plant evenly.
Farmers should check and clean the rice transplanter after each use. Regular oiling and inspection keep the machine running smoothly. Good care helps the machine last longer and work better.